Everything there is to know about the advantages of medical cloud computing for healthcare projects and organizations will be covered in this essay. We’ll also review software solutions that use cloud computing to manage healthcare data and some crucial factors to consider when integrating cloud computing into your healthcare systems.
What does cloud computing mean for the medical industry and other fields?
The provision of processing power and related services via the Internet, such as servers, scalable databases, networking, data storage, SaaS, data mining, and many forms of virtual intelligence and applications, is known as cloud computing.
Everything needed for quick innovation implementation and adaptable system resource scaling is provided by cloud computing. With the use of technology, healthcare initiatives and organizations can now…
- Store and distribute vast volumes of data without maintaining your own on-site data centers or high-end server PCs.
- Large volumes of data can be accessed or moved quickly, depending on the bandwidth and other channel factors.
- Integrate IoT, AI, ML, Big Data, connected medical devices, and other contemporary healthcare IT components.
- Avert or cut down on the price of buying and setting up pricey networking and server hardware.
What models of healthcare cloud computing exist?
Healthcare organizations utilize a variety of cloud computing service models.
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS): A medical organization can request access to a third-party technology provider’s physical facilities, which include servers, data centers, storage clusters, and other crucial IT equipment. Large and medium-sized businesses and projects that wish to save money on IT infrastructure and maintenance by deploying their proprietary systems in third-party data centers will benefit most from this strategy.
Software as a Platform (SaaS): A cloud provider enables the development, testing, deployment, and migration of healthcare software and services in a virtual, web-based environment using cloud infrastructure for medical organizations and/or tech contractors. By renting hardware and development tools rather than buying expensive server gear and executing apps locally, software developers can save money with this method.
Cloud Computing in Healthcare: the Current Situation
Cloud computing is becoming more and more relevant for healthcare organizations, as it has been widely utilized in this field. Roughly 90% of all businesses use cloud computing, either exclusively or in combination with other solutions (O’Reilly owns the original marketing data analysis). About 40% of respondents in the healthcare industry utilize private cloud solutions, 61% use public cloud, 27% favor hybrid cloud, and 19% choose multi-cloud computing apps.
Simultaneously, nearly half of the healthcare participants stated that they would prioritize cloud-first strategies wherever feasible, indicating that cloud technology would be their first choice for technological advancements and IT initiatives. “Managing costs:” is one of the most common justifications for cloud platform adoption in the healthcare industry.
The most widely used cloud computing applications in the medical field consist of…
Drug discovery: lab research, virtual molecular and formula modeling, chemical reaction simulation
Telemedicine includes online streaming for therapy sessions, video/audio surveillance, remote patient monitoring, and other Telehealth technology services.
- Access to information management systems can be both restricted and public.
- Shared knowledge databases and digital libraries
- The use of Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS) in medical facilities
- Virtual learning in universities and colleges of medicine
- Healthcare appointment-management systems, EHRs, and EMRs
- Systems for managing digital rights (DRM)
- Research and modeling on population health.
Nevertheless, 60% of healthcare companies continue to run their operations using some form of onsite, traditionally managed infrastructure (usually for legacy projects running parallel to newer cloud-based systems.) This figure might suggest that there is space for development and a significant move toward cloud services.
The Four Principal Advantages of Cloud Computing for Healthcare
- The healthcare sector can profit greatly from cloud computing in several ways, including
- enhanced capacities for sharing and accessing data
- improved productivity and efficiency of the medical system’s cooperation
- Interoperability of healthcare systems
- IT cost reduction and optimization
- Enhanced data security using intelligent elements
- adherence to regulations
- Data sustainability and speedy disaster recovery
- enhanced possibilities for patient care
- Scalability and potential for API-based integration.
Electronic Health Records: Streamlined Data Exchange and Access
The ability to quickly and easily derive and propagate patient data among medical systems is one of the main goals of cloud computing in the healthcare industry. Cloud-based solutions facilitate improved collaboration between healthcare providers across the United States and even abroad by enabling medical organizations to update and manage patient information in real time, regardless of their location.
EMR/EMR cloud storage, along with other healthcare software, empowers…
- optimized speed of data exchange and cost of data storage
- Instantaneous document and medical record synchronization
- Greater potential for designing and developing medical software Faster communication between remote healthcare organizations
- Higher data transmission security, as mandated by HIPAA
- Increased prospects for medical research and data mining
- improved patient status tracking with fewer mistakes resulting from out-of-date records.
Patients: Improved Clinical Experience and Safety
Medical organizations can obtain information and resources more quickly and easily with cloud-based healthcare solutions, which facilitate streamlined operations in diagnostics, medical history recovery, and enhanced patient care.
Patients can access telemedicine and analytical insights, among other top-notch healthcare services, through cloud-based solutions. They can:
- Get medical advice while lounging in their own homes.
- Take advantage of fewer in-person appointments
- Allow medical professionals more time to attend to other patients.
- Have faith that their medical professionals, when disclosing their records to authorized caregivers, will make knowledgeable decisions
- Track their medical statistics and treatment results over time.
- Receive technology-driven help from a distance, such as at-home real-time ECG monitoring.
IT Expenses: Infrastructure Savings
In the medical industry, cloud computing can also lower expenses for medical groups. Through the utilization of cloud-based solutions’ economies of scale, companies can lower their expenditures associated with IT, encompassing staffing, software, and hardware.
lower energy expenses as a result of data centers that are energy-efficient and created with less waste.
lower expenses for upgrades, maintenance, and purchases of hardware and software (all IT tasks are outsourced to cloud providers.)
- lower costs related to data storage charges.
- avoiding the hefty expenses connected to possible data breaches.
- Reduced expenses for developing medical software. Enhanced Security and Scalability in Data Management
- The healthcare sector benefits from enhanced data security and compliance thanks to cloud computing. Cloud-based solutions enable medical institutions to…
- Safely and in compliance with HIPAA regulations, store and retrieve patient data.
- Lower the possibility of data breaches and guarantee the security of patient data
- Take advantage of secure data exchange protocols, sophisticated authentication techniques, access tracking and logging, and other security features provided by cloud providers.
- Adapt the size of their IT resources to the demands of their projects.
Which Healthcare Sectors Use Cloud Computing?
It’s hard to find a medical specialty these days where cloud computing isn’t already in use. The range of cloud computing applications in the medical field is constantly expanding. Let’s examine the main areas of cloud computing in medicine.
Data management and storage Lab results, medical histories, doctor’s notes, and other medical data sharing in the context of EHRs and other medical systems.
- The management and fulfillment of e-prescriptions.
- Working together with health insurance companies and handling health claim administration.
- Big Data platform integrations and extensive medical data analysis for healthcare providers.
- Medical payroll apps and staff management in the healthcare industry.
- Applications of telemedicineSmart sensors and Internet of Things gadgets for patient monitoring from a distance.
- Portals for healthcare consultations for patients living far away.
- Alerts, notifications, and surveillance in real time.
- Advanced robotic systems and remote/virtual surgeries supporting medical professionals.
analytics for healthcare charts, graphs, software and device interfaces, and medical imaging are examples of medical data visualizations.
- Customized modeling of treatment plans.
- Claims processing is done with intelligence.
- Risk assessment and prognosis for epidemics and pandemics.
- CDSS, or clinical decision support systems
- Hospital administration automated supply-chain administration for healthcare establishments, such as hospitals and pharmacies.
Automation and synchronization of patient admissions, inventory turnover, and other hospital operations.
Accounting and financial management solutions, including integrations with medical payment systems; administrative reporting and bed management;
Three Examples: Cloud Computing’s Applications in the Pharmaceutical and Healthcare Sectors
The American healthcare sector is undergoing a revolution thanks to cloud computing, which has many advantages and is changing how healthcare institutions run.
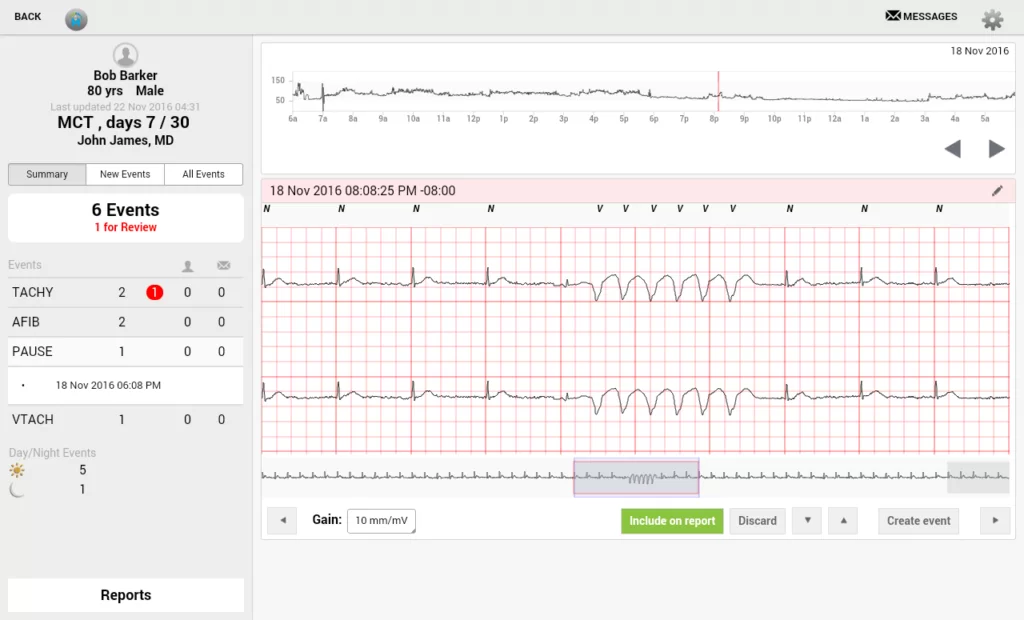
#1. Patient monitoring via remote Systems in the Cloud
The implementation of systems for remote patient monitoring and medical control is one of the most significant use cases of cloud computing in American and international healthcare. This idea allows doctors and other healthcare providers to keep an eye on the parameters and general health of patients who are not inpatients.
IoMT devices like sticky biosensors and data sharing between a particular client app on a patient’s smartphone and a server segment set up in the cloud (or any other possible IoMT configuration) are potential components of this project.
To process and send ECG data to healthcare providers (cardiologists) via professional apps installed on their iOS and Android tablets, this solution included cloud technologies for back-end APIs and a server application.
This complex solution consisted of…
- Visualization and profiling of patient ECG data
- Viewable on a scale for patient cardiogram data
- Automatic detection of a variety of irregular heartbeat patterns, including tachycardia and arrhythmia
- Effective synchronization between the server application and the mobile application.
#2. Cloud-based Solutions for Pharma Business Automation
Pharmaceutical companies can access and manage their orders, patient data, medication assets, prescription records, and more from any location by utilizing cloud-based systems. Pharma companies can easily add more capacity and devices as needed without worrying about infrastructure constraints or additional hardware procurement thanks to the scalability of cloud platforms.
Pharma firms can now handle rapid expansion and a high patient and prescription volume without having to make substantial IT investments thanks to the cloud.
We talked about the following:
- The client received a web application that combines data and product-management features with all important business operation processes via cloud services.
- The improved cloud-based order processing and data management workflows were presented to the client team.
- The client stated that faster order processing and prescription drug delivery resulted in improved financial performance.
- The client’s ability to integrate their system with the systems of their business partners for improved collaboration was made possible by the solution.
#3. Cloud-based Systems for Processing Insurance Claims
It is now feasible to create a cloud-based application with AI and ML components for the automated processing of health insurance claims because of contemporary methodologies and technologies. See Health Insurance App Development Guide: Potential Features, Costs, and Benefits for more information on the potential features of insurance apps, such as AI-backed fraud detection.
The project’s results are as follows:
- SCRx streamlined and expedited drug distribution procedures for both in-house and home delivery scenarios.
- They implemented cloud-based automated bulk PDF scanning and import for claims, which made it possible for them to achieve several significant advancements.
- We assisted them in putting into place an optical text recognition function, which enabled us to notify and alert their employees to new system alerts.
- SCRx used cloud computing and API tools to successfully bridge several systems.
Top Cloud Adoption Strategies for CEOs, CTOs, and CIOs of Healthcare Organizations
For the healthcare sector, several cloud computing best practices exist.
Begin with a well-defined plan.
CTOS must establish its cloud computing goals and objectives before diving into cloud computing solutions. This includes determining the particular needs of the company, such as…
- HIPAA compliance and other regulatory compliance
- Risks and security problems related to the cloud
- Selecting the ideal cloud service provider and providing
- Technical specifications such as uptime rate and storage volumes
Business sustainability, such as data consistency between various systems and uninterrupted business operations
Budget and time constraints are needed to set up a solution that satisfies every goal. Pay attention to privacy and security in the cloud.
Due to the sensitive nature of patient health information (PHI), strict security and privacy regulations are necessary. CTOs and other business executives ought to think about the following.
Features including data encryption, safe data storage, backup plans, and access control are among the security and privacy measures offered by the cloud provider.
Make sure their medical facility follows data security best practices, which include frequent backups and disaster recovery plans.
Frequent assessment and tracking of technical health indicators, performance, dependability, and efficiency of cloud solutions.
Verify that your cloud provider can scale your solution without sacrificing security or performance.
Possible Problems and Remedies with Cloud Computing in Healthcare
To ensure a safe and effective deployment, cloud computing in healthcare must address several obstacles and concerns. The dangers of cloud computing in the medical field consist of:
Ownership of data
Serious security and privacy concerns arise from the handling of extremely sensitive patient data by healthcare organizations. You genuinely have less control over your medical data when it is entirely stored in a cloud service. You should take serious legal precautions before transferring your data to the cloud. Legal professionals should carefully review the terms and conditions of vendor license agreements (EULA) for cloud services to make sure that all information is understood and that there are no major gaps or ownership compromises.
Dangers of data inaccessibility
Cloud-based medical apps won’t function as intended if a cloud system data center crashes unexpectedly or experiences extended outages (due to a natural disaster, for example). When essential medical systems, such as remote patient monitoring, experience an outage that lasts hours, it can turn into a serious emergency. Hybrid cloud strategies, which combine private and public cloud environments, are therefore necessary to reduce risk while reserving alternative capacities.
Issues with uptime and latency
There may be milliseconds (at most) of downtime between medical device commands and data exchange between healthcare applications because signals always take time to get to the cloud and back. This metric can have a significant impact on certain medical applications. For this reason, channels of communication need to stay steady and clear. Medical applications and devices need to adopt autonomous operation protocols to help withstand possible signal delays.
How Much Can You Save With Cloud-based Computing?
The amount that can be saved with cloud-based computing depends on the particular cloud solution being used, as well as the size and kind of healthcare organization. It’s crucial to outline the main ways that cloud computing can save medical institutions money by lowering their IT expenses.
Healthcare companies can do away with the need to spend money on pricey hardware and software thanks to cloud-based computing.
- Costs and staffing requirements for IT are also decreased.
- Pay-as-you-go cloud-based services can be subscribed to by medical organizations, lowering the upfront costs of IT products and services.
- lower energy costs as a result of cloud technologies being supported by power-efficient data centers.
- The economy of scale is attained through pooling cloud resources with other businesses.
Conclusion
Making healthcare a top priority not only guarantees better health now but also prepares the way for a stronger, more rewarding future. Accept the transformative power of health to achieve long-term well-being and an improved quality of life.
Moreover, if you are looking for a healthcare software development company through which you can hire developers, then you must check Appic Softwares. We have an experienced team of developers that can assist you in building medical software. You can even hire dedicated developers from us and let them manage your billing software.
So, what are you waiting for?








